History
- 2016 The 50th anniversary of the foundation.
- Apr 2015 Collaborative research division “Condensed Matter Nuclear Reaction” established.
- Jul 2014 Research building renovated and the Mikamine Hall completed.
- Dec 2013 Operation resumed after recovery from the Great East Japan Earthquake.
- Apr 2011 Approved as a Joint Usage/Research Center for Electron Photon Science.
- Mar 2011 Operation suspended due to damages by the Great East Japan Earthquake.
- Mar 2010 “Accelerator-based Light Source Building” completed.
- Dec 2009 Reorganized as “Research Center for Electron Photon Science”.
- Sep 2009 Electromagnetic calorimeter “FOREST” completed in the Gamma-ray Irradiation Room.
- Feb 2008 “High-frequency Power Source Building” completed.
- Sep 2006 Magnetic electrometer “NKS2” completed in the Second Experimental Room.
- May 2006 Electron-Positron test beam line operation started.
- Jul 2002 GeV Gamma-ray Irradiation building completed and started Hadron experiments.
- 1998 Organized as adjunct facility of Graduate School of Science.
- 1997 1.2 GeV Stretcher Booster Ring completed.
- 1988 World’s first observed coherent emission.
- 1982 150 MeV Pulse Stretcher completed.
- 1971 Pulse neutron source developed.
- 1967 300 MeV Electron LINAC completed.
- 1966 Established as an on-campus shared-use facility in nuclear physics.
Member
Academic staff list (RARIS-Mikamine)
| Name | Title | Research field | tel | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hiroaki OHNISHI | Professor (Director of RARIS) | Quark Nuclear Physics | ohnishi | 3423 |
| Norihito MURAMATSU | Professor | Quark Nuclear Physics | mura | 3416 |
| Shigeru KASHIWAGI | Assoc. Prof. | Beam physics/Accelerator Science | kashiwagi | 3434 |
| Hidetoshi KIKUNAGA | Assoc. Prof. | Radiochemistry, Nuclear Chemistry | kikunaga | 3425 |
| Fujio HINODE | Assoc. Prof. | Beam physics/Accelerator Science | hinode | 3424 |
| Yukie Maeda | Assoc. Prof. | |||
| Manabu MIYABE | Assis. Prof. | Quark Nuclear Physics | miyabe | 3435 |
| Atsushi TOKIYASU | Assis. Prof. | Quark Nuclear Physics | tokiyasu | 3422 |
| Yuki HONDA | Assis. Prof. | Exotic Nuclear Physics | honda | 3417 |
| Yuji MATSUMURA | Assis. Prof. | Quark Nuclear Physics | matumura | 3435 |
| Takuya YOKOKITA | Assis. Prof. | Radiochemistry, Nuclear Chemistry | yokokita | 3436 |
| Jirohta KASAGI | Research Prof. | Nuclear Physics, Condensed Matter Nuclear Reaction | kasagi | 3414 |
| Hajime SHIMIZU | Research Prof. | Quark Nuclear Physics | hshimizu | 3414 |
| Hiroyuki HAMA | Research Prof. | Beam physics/Accelerator Science | hama | 3432 |
| Toshimi SUDA | Research Prof. | Exotic Nuclear Physics | suda | |
| Takehiko ITOH | Research Prof. | Quark Nuclear Physics | itoh@lns.tohoku.ac.jp | 3426 |
Academic staff list (Tohoku Univ.)
| Name | Affiliation / Titele | Research fields |
|---|---|---|
| Hirokazu TAMURA | Graduate school of Science, Department of physics, Professor | Experimental Nuclear physics group |
| Koji MIWA | Graduate school of Science, Department of physics, Assoc. Professor | Experimental Nuclear Physics group |
| Masashi KANETA | Graduate school of Science, Department of physics, Assoc. Professor | Experimental Nuclear Physics group |
| Shoichi Sasaki | Graduate school of Science, Department of physics, Assoc. Professor | Nuclear Theory |
| Yasushi KINO | Graduate school of Science, Department of chemistry, Professor | Radiation Chemistry |
| Nobuyuki UOZUMI | Graduate school of Engineering, Department of physics, Professor | Biomolecular Engineering |
Office
| Name | Tel | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Office | kakurike | @ | grp.tohoku.ac.jp | 3400 |
| Radiation Safety Office | kanri | @ | lns.tohoku.ac.jp | |
Facilities
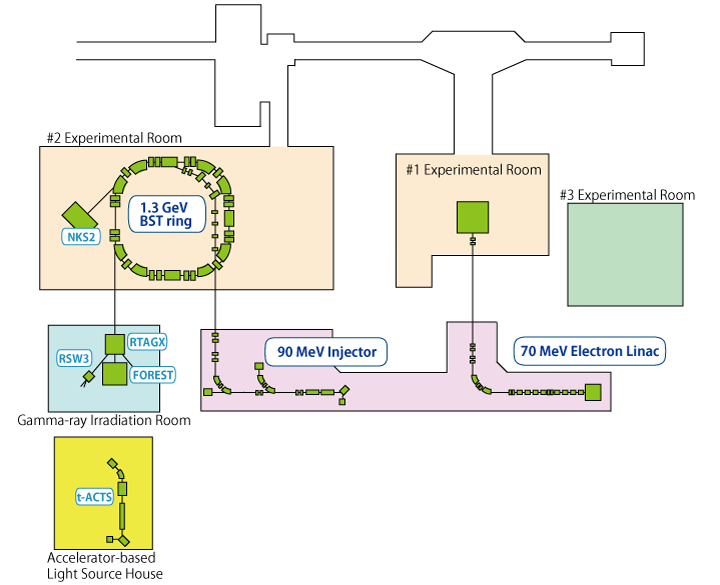
Accelerators and Beam properties
In ELPH, the electron and photon beam lines are provided for nuclear physics experiments and a radioactive isotope production. (Present Configuration (2015))High intensity electron linac

| Linac Energy | Modulator Repetition | Macropulse Peak Current | Macropulse Duration | Average Current |
| 50 MeV | 300 Hz | 〜130 mA | 3.0 µs | 120 µA |
| 30 MeV | 300 Hz | 〜100 mA | 3.0 µs | 90 µA |
Injector linac for BST

1.3 GeV Booster-STorage ring (BST)

BST is an electron synchrotron which accelerates the electrons injected from the injector linac up to 1.3 GeV in maximum. The required energy to accelerate and store the electron beam is supplied by a 500 MHz rf cavity. By inserting a very fine carbon wire to the beam orbit of circulating electrons after the acceleration, high energy gamma rays are generated via bremsstrahlung. Two beam lines are operational to utilize such gamma rays. In a typical operation pattern, beam acceleration is immediately started just after the injection and finished within ~2 sec., and then stored electrons with ring current of 10~30 mA are consumed to generate the gamma rays over a duration of about 10~40 sec. Currently available operation energy is 1.3, 1.0 and 0.8 GeV, and typical ring current is ~10~30 mA.
| Injection Beam Energy | Injection Repetition | Ring Top Energy | Storage Beam Current |
| 90 MeV | ~0.05 Hz (typ.) | 0.8~1.3 GeV | ~30 mA |
Tagged photon beamline
The BST ring has two beamlines providing tagged photons. The typical properties of the tagged photon beams are summarized in the table:| Beam line | Energy Range (Rint Energy: 1.3 GeV) |
# of Bins | Intensity | Duty |
| BST-Tagger-I | 0.8 ~ 1.26 GeV | 160 | TBC | ~60% (NKS2) |
| BST-Tagger-II | 0.9 ~ 1.25 GeV | 116 | TBC | ~50% (FOREST) |
Photon beamline I
The photons are designed to be tagged with energies of 62%~98% with respect to the circulating electron energy of the BST ring. The number of tagging channels are 160. The details of the photon beam properties are under investigation.
Please contact to Dr. M. Kaneta (mail: kaneta@lambda.phys.tohoku.ac.jp).
Photon beamline II
The photons are designed to be tagged with energies of 62%~96% with respect to the circulating electron energy of the BST ring. The duty facto is approximately 50% (stable photon beam can be obtained for 8.5 s out of a 17 s cycle). The number of tagging channels are 116. The details of the photon beam properties are under investigation. Information before The Great East Japan Earthquake (March 11, 2011) can be obtained in a reference "The second GeV tagged photon beamline at ELPH"Reference: T. Ishikawa et al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A 622, 1 (2010).
Please contact to Dr. A. Tokiyasu (tokiyasu-at-lns.tohoku.ac.jp -at- should be replaced with @).
Positron/electron beamlines for testing detectors
The positrons and electrons, which are produced at a metal plate in front of the bending magnet RTAGX by the photon beam, are provided at three beamlines in the GeV-γ experimental hall. The positrons and electrons are momentum-analyzed with RTAGX, and the energy spread of them is approximately 0.5% . The beam profile and intensity depend on the beam energy, and the diameter of the beam is roughly 20 mm, the intensity is roughly a few kHz. The positrons (or electrons) at the -30 deg beamline can be focused with a triplet quadrupole magnets thanks to a KEK cooperation. The polarity of the magnets can be changed. The details of the photon beam properties after the earthquake are under investigation. Information before can be obtained in a reference "A detailed test of a BSO calorimeter with 100-800 MeV positrons",Reference: T. Ishikawa et al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A 694, 348 (2012).
| Beam | Beam line | Maximum beam energy |
| Positron / Electron | ± 30 deg | ~840 MeV |
| Positron | -23 deg | ~1000 MeV |